How to identify electrical cable sizes
The size of a cable depends on the size of the conductors. The following are the methods by which the size of a cable or conductor is determined:
(1) With a standard wire gauge,
(2) according to the diameter of the conductor and
(3) according to the cross-sectional area of the
conductor. Wire Sizes: Copper wires are expressed in numbers/ wire
gauges system, e.g., 3/22,3/20,7/22,7/20 etc. 3/22 system means a cable has 3
wires of 22 S.W.G. The Standard Wire Gauge (S.W.G.) or American Wire Gauge
(AWG) are commonly wire gauges. Aluminium wire diameters are measured in
millimeters in the metric system. The crosssectional areas are calculated and
now-a-days as per Indian standard Aluminium wires are expressed with area in
millimetre square e.g.,1.5 mm2, 2.5 mm2 etc. 1.5 mm? means a cable conductor
has its area cross-sectional equal to 1.5 mm2 with a diameter of 1.38 mm. A 7
strand cable/wire whose each strand is .085 mm dia. has a total 4 mm2 area of
total 4 mm2 area of cross-section. It is expressed as 7/0.85 mm. In the same
way 7/1.35 mm has 10 mmcross-section. See table at the end of this book.
Standard Wire Gauge :
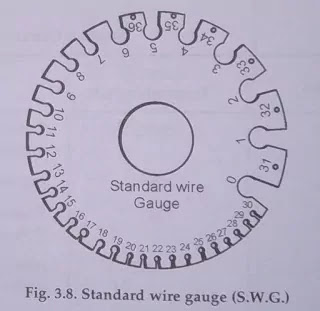
The Standard Wire Gauge (S.W.G.) is a device which is used for determining the size of a wire. The wire gauge commonly used in India is the British standard wire gauge. It consists of a thin circular strip plate of steel with a number of slots on its circumference as shown in Fig. 3.8. Each slot is marked with different numbers. Holes are provided at the end of each slot for removing the wire easily.
distance transmission lines ?
Ans.
(a) The cable (some overhead bare copper conductor also) number of strands of wire of circular cross-section, so that
(1) it may become flexible,
(2) carry more current and
(3) can have more breaking strength.
(b) Stranded aluminium conductor with steel wire in the centre (Reinforced) (S.A.C.S.R.) is used for H.T. long distance transmission. For more details
please see Overhead Line chapter.
Various Types of Wires :
These wires are used for outdoor work as service lines. The conductors are insulated first with rubber, then braiding of cotton thread. The braiding material is dipped in waterproof compound.
These wires are used for giving connection to heating appliances, pendent lights, portable appliances etc. The insulation used is pure rubber or vulcanised rubber or which single or double cotton or vulcanised rubber on which single or double cotton or artificial silk braiding is providing or only PVC is used. Following are the types of flexible wires available in the market:
1. T.R.S. flexible wires.
2. Workshop flexible wires available in 3 core and 4 core
(three phase and neutral wires).
3. P.V.C. Insulated Flexible wires.
(a) Vulcanised rubber insulated wire,
(b) Eureka wire,
(c) Nichrome wire,
(d) Hard drawn bare copper conductor,
(e) Aluminium conductor,
(f) Enamelled wire.
or which should be covered by some protection, not in use now-a-days.
(b) Eureka wire : It is used in rheostates which are used for variable resistance
in the circuit.
(c) Nichrome wire : It is used as a heat-producing resistance in heating appliances.
(d) Hard-drawn bare copper conductor: It is used in over-head lines and earth
connection wires.
(e) Aluminium conductor: It is used in overhead lines now-a-days. It is used as
well in V.I.R. wires, C.T.S. wires and P.V.C. wires.
(f) Enamalled wire: It is used for winding all types of electric motors and
generators. It is also used for making electro magnets.
1. P.V.C. flexible wire twin twisted.
2. P.V.C. flexible wire two core.
3. P.V.C. flexible wire three core.
4. Cotton covered flexible wire twin twisted.
5. Silk covered flexible wire twin twisted.
6. Cotton covered flexible wire 2 core/3core.
7. T.R.S. or P.V.C. flexible wire 3core/4core.
Voltage Grades:
Low voltage - upto 250 V
Medium voltage - 251 to 250
High voltage - 651 to 33 kV
Extra High Voltage - above 33 Kv.
THANKING YOU








No comments:
if you have any doubts,please let me know